History of DNA Discovery Timeline Infographic Template
Discover the fascinating history of DNA and its monumental impact on modern science by creating your own timeline!
100% customizable templates
Millions of photos, icons, charts and graphics
AI-powered editing features
Effortlessly share, download, embed and publish
Easily generate QR codes for your designs
- SizeLetter (8.5 x 11 in)
- File typePNG, PDF, PowerPoint
- Planpremium
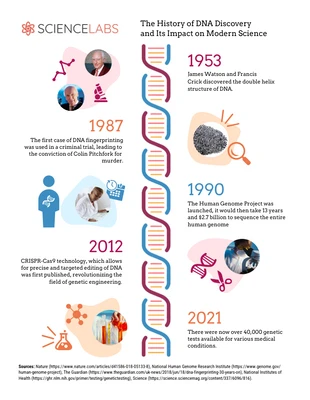
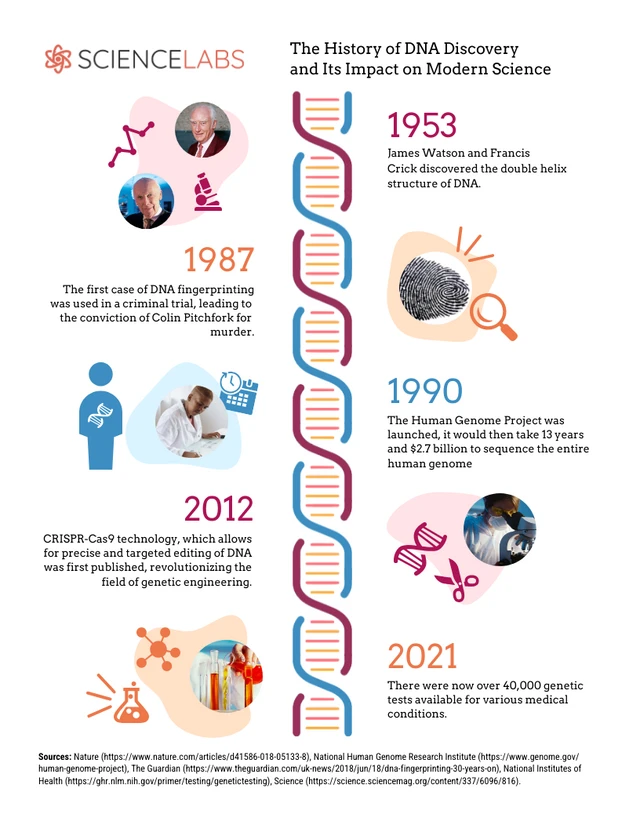
DNA's discovery began with Friedrich Miescher's identification of nuclein in 1869. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed the double helix model, revolutionizing genetics. DNA sequencing advancements, such as Sanger sequencing, allowed gene mapping and manipulation, enabling genetic engineering and genomics. The Human Genome Project (1990-2003) further accelerated DNA research, contributing to personalized medicine, gene therapy, and forensic applications. DNA technology has profoundly impacted modern science, spurring interdisciplinary collaborations and discoveries across biology, medicine, agriculture, and numerous other fields.